Railroad Modelling Scales
Summary: Model railway scales are standardized worldwide by many organizations and hobbyist groups. The two dominant standards organizations are NMRA in North America and MOROP in Europe with its NEM standard.

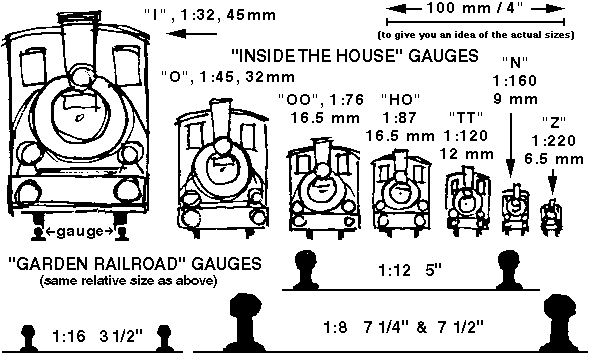
Model railway scales are standardized worldwide by many organizations and hobbyist groups. Some of the scales are recognized globally while some others are less wide-spread and in many cases, virtually unknown outside their circle of origin. Globally the two dominating standard organizations are NMRA in North America and MOROP in Europe with its NEM standard. The majority of commercial model railway equipment manufacturers base their offerings on NEM or NMRA standards in the most popular scales. Worldwide, the most popular scales are HO, N, O, G, TT and Z. In addition to these, there are several less well known scales, significant in their own speciality areas such as live steam garden railroading, or simply garden railroads.
The terms scale and gauge are often confusingly misplaced in model railways, but there is an important difference. Scale means the ratio between a unit of measurement on a model compared with a unit of measurement in corresponding full size prototype. Gauge, on the other hand, is the distance between the two running rails of the track. In full size prototype, a railway may have tracks of standard gauge (1435mm or 4'8½" in most countries), but there are also narrow gauge railways and even narrower industrial railways. In a similar manner, a scale model railway may have several track gauges in one scale.
History of Scale Standards
Also see Model Railroad Scales for more info and history.
The first model railways were not built to any particular scale and were more like toys than miniature representations of the full size prototype. Eventually, the authenticity of models grew and benefits of standardization became more obvious. The most significant and the most basic area of standardization was the model gauge. At first, certain track gauges became de facto standards in hobbyist and manufacturer circles. While the first unofficial standard gauges made interchangeability possible, the rolling stock were still only a rough approximation of the full scale prototype.
Eventually the unofficial or manufacturer specific scale standards became more established and were adopted by various model railway standardization bodies such as NMRA and MOROP. However, despite of existing scale and gauge standards they were very often poorly implemented in design and manufacturing processes with commercial manufacturers before the World War II. The conformity to scale standards grew strongly in the 1950's and 1960's when many new model railway accessories manufacturers were born and to whom the standard conformity was vital.
It should be noted, that for most standardized model railway scales, the nominal scale reduction ratio is not applied systematically to all the components of a scale model railway and normally the standards give scale specific design guidelines for all the scales they cover. Reliability of operations requires certain parts to be designed oversized. A typical example are the wheel flanges which must be proportionally higher in smaller scales to ensure that lighter and smaller models do not derail easily which would be the case if universal flange proportions were used in all the scales. For instance, a Z scale wheel flange as defined in the NEM-standard should be about 9% of the scale nominal standard gauge (6.5mm) whereas the same standard gives the 45mm standard gauge I scale only 5%.
While standards that put the emphasis on operational reliability, satisfy most users and the industry, certain groups of dedicated hobby modellers who were dissatisfied with the scale inaccuracies in the name of reliability, developed alternative scale standards where the proportions of the full size prototype were maintained as much as possible. These alternative standards are called finescale standards. Finescale standards are very much restricted to hobbyists circles since, by definition, finescale model railway is generally less reliable and more expensive to manufacture which makes it unsuitable for mass production marketed to consumers. However, there are some commercial finescale manufacturers that produce remarkably detailed and expensive handmade scale miniatures for connoisseurs in small series.
Scales
| Name | Size/Scale | Gauge in mm |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grand Scale | 1:4 and up | 254 mm and up | Several large scales exist, but are not strictly model railroading gauges. Instead, they are used mostly in commercial settings, such as amusement park rides. |
| Live Steam | 1:8 | 184 or 190 | Ridable, outdoor gauge, named according to the gauge in inches, and scale in inches per foot, for example 7-1/4" gauge, 1.5" scale. The gauge is 7-1/2" in the western parts of US and Canada, where the scale sometimes is 1.6" for diesel-type models. Private and public (club) tracks exist in many areas, among them the world's largest model railroad, Train Mountain, with over 25 miles (40 km) of tracks. Powerful locomotives can pull 50 or more passengers. Narrow gauge models in this gauge can be as large as 1:3 scale. |
| Live Steam | 1:12 | 127 or 121 | Ridable, outdoor gauge. The gauge is 5" in Europe, but 4-3/4" in US and Canada. Together with the 1:8 scale above, this is a popular scale for backyard railroads. Pulling power is enough for more than a dozen passengers on level tracks. |
| Live Steam | 1:16 | 89 | Ridable, outdoor gauge. The gauge is 3-1/2" the world over. |
| Live Steam | 1:24 | 63 | The smallest of the "ridable" gauges. Can only pull one or two passengers. This was one of the first popular live steam gauges, developed in England in the early 1900s, but it has become more or less obsolete because of the larger gauges. |
| Wide gauge | 1:26.59 or 1:28.25 | 53.975 | Called Standard Gauge by Lionel, who trademarked the name. Other manufacturers used the same gauge and called it Wide Gauge. Not widely produced after 1940. Gauge No. 2 using track of gauge 2" (50.8 mm) was one of the standard model gauges in 1909. |
| 16 mm scale | 1:19.05 | 32 | This scale was first developed in the UK in the 1950s to depict 2 foot narrow gauge prototypes utilising 32 mm or "O gauge" track and wheels, but really took off in popularity during the 1960s and 70s. Originally, it was mostly used as an indoor modelling scale, but has also developed as a popular scale for garden railways of narrow gauge prototypes. Some manufacturers that produce models depicting North American 2 foot narrow gauge prototypes have also adopted this scale for use alongside the near-compatible Fn3 (15 mm) scale on 45 mm track already popular in the US. Both electric, battery and live steam propulsion is used to power model locomotives in this scale, and is supported by a growing range of commercially available ready-to-run models, kits and parts. |
| Fn3 scale | 1:20.3 | 45 | Similar to G Scale below, this scale also 45 mm gauge track, and used for both indoor and garden railways of narrow gauge prototypes. The scale of 1:20.3 was developed to depict North American 3 foot gauge trains in exact proportion to their correct track gauge whilst using 45 mm gauge model track. It equates to 15 mm = 1 foot scale. Increasingly popular for both electric and live steam propulsion of model locomotives, with an ever growing range of commercially available ready-to-run models, kits and parts. Fn3 scale, together with G scale and ½" scale, are commonly and collectively referred to as "Large Scale" by many modellers. |
| G scale | 1:22.5 | 45 | Name derived from 'G'ross, which means "big" in German. G is generally used for garden railways of narrow gauge prototypes, and uses the same track gauge as Gauge 1 below. The scale of 1:22.5 scales the trains correctly for the European narrow gauge standard of 1 metre. That is gauge 3 scale on gauge 1 track. 1:22.5 on G gauge track is known as LGB after the initials of the name used for it by the main manufacturer Lehmann Gross Bahn. |
| ½" scale | 1:24 | 45 | Similar to G Scale above, this scale also runs on 45 mm gauge track, and is generally used for both indoor and garden railways of narrow gauge prototypes. The scale of 1:24 in combination with 45mm track is an attempt to model North American and UK 3 foot or 3 foot 6 inch narrow gauge trains in better proportion to the rails they run on. |
| Gauge 1 or I scale 3/8" scale |
1:32 | 45 | This large scale, once rarely seen indoors in modern use but frequently used for modelling standard gauge trains outdoors, is making a come-back. The Japanese firm of Aster offers ready-to-run gas-fired livesteam models. Gauge 1 has seen something of a remarkable revival in recent years after decades of near extinction commercially, with a growing number of smaller UK manufacturers offering electrically powered locomotive and rolling stock kits and parts for (mostly) indoor layout use. Some manufacturers offer so-called Gauge 1 items in 1:30.48 scale (10 mm = 1 foot) that also run on 45 mm gauge track. |
| L gauge | 1:38(nominal) | Unofficial designation of toy trains built from LEGO®. Equipment can be built to differing widths in relation to the track gauge, and are becoming increasingly popular among persons who grew up with the building toy system. | |
| O scale | 1:43.5 or 1:45 (Eur) 1:48 (US) |
32 | Name originally was '0' (zero), '1' through '6' were already in use for larger scales. In the US, this is frequently a 'toy train' scale rather than for exact scale modellers. In the US practice, the track is wider, resulting in a model that is smaller as the track is 1:43 and the rolling stock is 1:48. |
| Q Scale | 1:45 | 32 | Modified version of 0 Scale, based on 17/64" (0.2656") = 1 foot |
| Proto:48 | 1:48 | 29.90 | These are to the same scale as US O gauge but are accurate scale models in all dimensions including track and wheels. |
| ScaleSeven | 1:43.5 | 33 | Exact scale version of British O gauge. |
| S gauge | 1:64 | 22.42 | Originally called "H-1" because it was half the size of Gauge 1 (1:32), the "S" name is derived from 'S'ixty-fourth. In the US, American Flyer toy trains are to this scale, but it is also used for more precise modelling and supported by several manufacturers. In the UK, S scale modelling is largely the preserve of a dedicated few hand-building models or using a small number of available kits and parts, mostly depicting standard gauge prototypes but also narrow and broad gauge subjects too. The UK-based S Scale Model Railway Society is the oldest scale support society in the world, being first established in 1946. This scale is also popular in North America to depict 3 foot narrow gauge prototypes (using dedicated 14.28 mm gauge track and known as "Sn3"), and elsewhere to depict the 3 foot 6 inches narrow gauge railways (using HO 16.5 mm gauge track and known as "Sn3½") of South Africa, Australia and New Zealand. |
| OO gauge | 1:76.2 | 16.5 | This scale is today the most popular modelling scale in the UK, although it once had some following in the US (on 19 mm gauge track) before WW2. OO or "Double-Oh", together with EM gauge and P4 standards are all to 4 mm scale as the scale is the same, but the track standards are incompatible. OO uses the same track as HO (16.5 mm gauge), which is not correct for this slightly larger scale, but it is the most common British standard for ready-to-run trains. In Britain there exists The Double O Gauge Association to promote this scale. Narrow gauge modelling of 3 foot prototypes ("OOn3" on 12 mm track) was once popular although now less so, but the depiction of approximately 2 foot or 2 foot 6 inch prototypes ("OO9" on 9 mm track) has a greater following with a flourishing supply of kits and parts from many small UK-based suppliers. |
| EM gauge | 1:76.2 | 18 | EM gauge was an earlier attempt in the 1950s to improve the inaccuracies of OO gauge, with wider, more accurate track at 18 mm between the rails, but still narrower than the correct gauge. Many early finescale modellers in the UK used this standard and it is still in use (albeit with the gauge now slightly adjusted to 18.2 mm), although P4 has superseded it for most. The UK-based EM Gauge Society exists to supports modellers of these standards. |
| P4 Standards | 1:76.2 | 18.83 | During the early 1960s a group of British modellers evolved a finescale standard at 4 mm to the foot with near exact scale track and wheels. This was later formalised by the founding of the Protofour Society which attempted to exercise strict control over the manufacture of specialised parts to these standards. A separate group, the Scalefour Society, was formed in the 1970s promoting an even finer exact scale standard called S4, but encouraged a wider group of manufacturers to support its aims. Later, in the 1980s, sanity prevailed and both societies merged, adopting the original P4 standards by which it continues to be known (and not S4), but encouraging a wide manufacturing base and retaining the society name of Scalefour. The "P" stands for "Proto[type]" and these standards are intended to be applied to any prototype gauge in 4 mm scale, which for standard gauge track happens to work out at 18.83 mm. P4 standards have also been used to depict narrow and broad gauge railways on a variety of model gauges. In the UK many kits include parts to enable them to be built to OO, EM or P4 gauges and there is a flourishing "cottage industry" of small business kit and parts suppliers. EM gauge was an earlier attempt to improve OO with the more realistic (but still inaccurate) gauge of 18 mm (later 18.2 mm). |
| HO scale | 1:87 | 16.5 | This is the most popular model railway scale in the world (except in the United Kingdom). The name is derived from "Half 0" and the Normen Europäischer Modelleisenbahnen (NEM) define the scale as exactly 1:87, the US NMRA as 1:87.1 (3.5 mm : 1 ft). Derived from the European 1:43.55 0 Scale (7mm/foot). Not surprisingly, there is a vast selection of ready-to-run, kits and parts for locomotives, rolling stock and scenic items from many manufacturers depicting trains from all around the world. Narrow gauge modelling of North American 3 foot gauge ("H0n3" on dedicated 10.5 mm track) and 2 foot gauge ("H0n30" - actually 30 inch gauge - on 9 mm track), European metre gauge ("H0m" on 12 mm track) and 750/760 mm gauge ("H0e" on 9 mm track) has become very popular. In Britain, H0 was popular before WW2 but lost out to OO and it virtually disappeared from the modelling scene, except for those modelling European and North American prototypes. A few commercial models depicting British prototypes were manufactured during the 1970s (usually in error or ignorance by foreign firms), which, together with a few items suitable for conversion to British outline, prompted some modellers to revive British H0 modelling in the 1980s, culminating with the establishment of the British 1:87 Scale Society in the mid-1990s. Today, British H0 is making a modest come-back. |
| Proto:87 | 1:87 | 16.5 | An alternative finescale standard for HO, with wheels and track that correspond with the prototype's, taking its lead from the establishment of P4 standards in the UK. |
| 3mm Scale | 1:101.1 | 12 and 14.2 | A UK version of TT introduced by the firm Tri-ang in the late 1950s (then known as "TT-3") and supported by several other firms offering kits and parts. Commercial production by Tri-ang petered out in the late 1960s, but "The 3mm Society" was established in 1965 and a dedicated membership has kept this UK scale alive. TT-3 was originally designed to run on TT's 12mm gauge track, but latterly the more accurate gauge of 14.125mm (popularly known as "14.2") has been adopted by some seeking more accuracy. Like the intermediate EM gauge standard in 4mm scale, some modellers in 3 mm scale developed 13.5mm track gauge, but this has largely been superseded by 14.2mm gauge. Both 3 foot narrow gauge (using 9mm gauge track) and Irish 5 foot 3 inch broad gauge (using 15.76mm gauge track) are also modelled in 3mm scale in the UK. |
| TT scale | 1:120 | 12 | Name stands for 'Table Top' - no longer widely used but making a come-back. There is a small following in the US, and a large following in Germany, especially in the former DDR. |
| N Scale UK | 1:148 |
9 | As with 1:160 N scale below, the name is derived from its Nine millimeter track gauge, but the scale is a slightly larger at 2 1/16th mm = 1 foot. Developed as a UK commercial version of N scale in the late 1960s, models are restricted to depicting UK prototypes. Although nominally to 1:148 scale, some manufacturers took significant liberties with exact scale to suit production limitations. Despite the collapse of Graham Farish and its subsequent sale to Bachmann Industries there is a growing choice of ready-to-run models available. A few commercial kits and parts to fit Z scale loco mechanisms and wheels are offered by the UK firm Peco to enable narrow gauge prototypes to be modelled. May also be known as OOO Scale |
| N Scale Japan | 1:150 |
9 | N scale in Japan is normally built to this scale, even though most rail lines are narrow gauge (3'6"). Because the Bullet train lines are standard gauge (4'8 1/2"), models of these are usually built to the scale of 1:160. |
| 2 mm scale | 1:152 | 9.42 | British finescale standard, older than N scale, being first used as long ago as 1927 with photos and articles published in the model press. Became more popular in the 1950s, with The 2mm Scale Association established by 1960 to promote and support modellers in this tiny scale, and it remains very active in the UK to this day. In recent years the finer track and wheel standards of 2 mm scale (but not the gauge) have also been adapted for use in 1:160 N scale (on 9 mm gauge) in Europe and called "fiNe", and is supported by the FREMO modelling organisation. Since the 1950s, incredibly, 2 mm scale has been used to depict narrow gauge prototypes on various track gauges down to 4 mm, but almost everything has to be hand-made, unless some Z scale parts are used. |
| N scale | 1:160 |
9 | Name derived from Nine millimeter; this is the second most popular scale worldwide. N scale developed by the German firm of Arnold Rapido in the early 1960s, and was rapidly adopted worldwide as the most popular small-scale modelling choice. In recent years, finer profile wheels and track have been developed by some manufacturers (although the gauge and standards have remained the same). Huge range of ready-to-run models available as well as supporting kits and parts. With the introduction of an even smaller Z scale in 1972, the modelling of narrower gauge prototypes has been possible using that scale's locomotive mechanisms, track and wheels. In North America the depiction of 3ft gauge railroads in N scale using Z scale track is known as "Nn3"; in Europe, metre gauge modelling in N scale is known as "Nm". |
| Z gauge | 1:220 | 6.5 | Until recently the smallest commercially available model railway scale, introduced by the German firm of Märklin in 1972 depicting German and other European prototypes. In North America the firm of Micro Trains and others has introduced a range US prototype models. On both continents, a growing range of kits and scenic accessories has become available to help increase its popularity. In Europe a few enterprising manufacturers have developed even smaller metre gauge models (but still in 1:220 scale) known as "Zm" on 4.5 mm gauge track, in this smallest of commercial scales. |
| ZZ scale | 1:300 | 4.8 | Introduced by Bandai the ZZ scale is the smallest commercially available model railway available today. As of 2005 only three Shinkansen trains are available and limited other items. In comparison Z scale offers a wide range of products and accessories. |
Here is a handy scale converter for creating a more accurate layout when trying to determine if a car will match your scale size.
To see how the different scales are used, please check out the layout styles category.
See Also
External links
- http://www.spikesys.com/Modelrr/scales.html – Contains more specifics about some of the scales