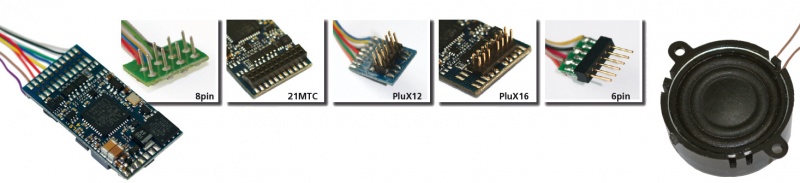
Locomotive Interface
Summary: The NMRA and NEM adopted standard mechanical and electrical interfaces to connect Multifunction Decoders to a locomotive's electrical system. These plugs and sockets make it simpler to install a decoder into a suitably equipped locomotive. In many cases a blanking plug must be removed before installing the decoder. If a locomotive is not DCC-Ready it will lack an interface and must use a Hardwired Decoder or a drop-in replacement DCC control board (if available) for that specific model.
|
See the Video. |
NMRA and NEM Connectors
- Main article: Locomotive Interface/NMRA Eight Pin Plug
| Name | NMRA | NEM |
|---|---|---|
| 4 Pin | NMRA Large | NEM 654 |
| 6 Pin | NMRA Small | NEM 651 |
| 8 Pin | NMRA Medium | NEM 652 |
| 21MTC | 21MTC | NEM 660 |
| Next18/Next18–S | Next18/Next18–S | NEM 662 |
| PluX | PluX8/16/22 | NEM 658 |
NMRA and NEM 6, 8 and 4 Pin Interfaces
The NMRA is discouraging the use of the 4, 6 and 8 pin interfaces in new models.
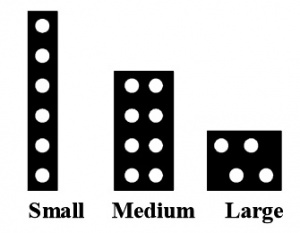
These interfaces are designed for basic installations without sound or many additional functions. The various sizes are intended to cope with the various physical size and power requirements for different scales.
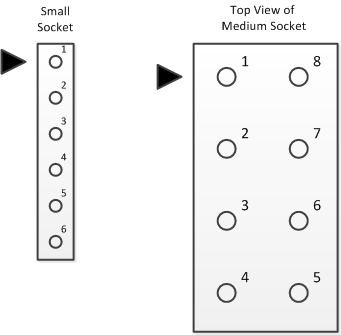
The 6 pin small interface is intended for N gauge locomotives due to their restrictive size and lower power requirements. The locomotive side is a 1x6 female socket with 0.05" pitch. It is also called a NEM 651 plug.
The 8 pin medium interface is intended for HO/OO gauge locomotives and allows for slightly higher power and simplifies headlight wiring. The locomotive side is a 2x4 female socket with 0.1" pitch. Also known as the NEM 652 plug.
The 4-pin large interface (NEM 654) is intended for O gauge and above and allows for higher power. The locomotive side is 4 male pins, the decoder side is 4 female sockets. The standards do not define the physical connector layout.
Pin Assignments and Wire Colours
| PIN ASSIGNMENTS BY COLOUR | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| DCCWiki.com | |||
| These Connector Types are now Obsolete. | |||
| Pin # | Small, Six Pin | Medium, Eight Pin | Large, Four Pin |
| 1 | Orange | Orange | Grey |
| 2 | Grey | Yellow | Orange |
| 3 | Red | Output 3 / Aux 1[1] | Black |
| 4 | Black | Black | Red |
| 5 | White | Grey | N/A |
| 6 | Yellow | White | |
| 7 | N/A | Blue | |
| 8 | Red | ||
Six and Eight Pin Interface
| Six Pin Socket Interface | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reference | S-9.1.1.1 | |
| DCCWiki.com | ||
| Pin | Description | Colour |
| 1 | Motor (+) | Orange |
| 2 | Motor (–) | Gray |
| 3 | Right Rail | Red |
| 4 | Left Rail | Black |
| 5 | Headlight, Front | White |
| 6 | Headlight, Rear | Yellow |
| Eight Pin Socket Interface | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reference | S-9.1.1.1 | |
| DCCWiki.com | ||
| Pin | Description | Colour |
| 1 | Motor (+) | Orange |
| 2 | Headlight, Rear | Yellow |
| 3 | Output 3 / Aux 1[1] | Green |
| 4 | Left Rail | Black |
| 5 | Motor (–) | Gray |
| 6 | Headlight, Front | White |
| 7 | Common (V+) | Blue |
| 8 | Right Rail | Red |
NMRA S-9.1.1 Decoder Interfaces
| Wire Colour | Function | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Right-hand rail power pick-up: Center rail, outside third rail, traction/overhead wire to motor or interface | 1 |
| Orange | Interface to Motor + (Postive) | |
| Black | Left hand rail power pickup to motor or interface | |
| Grey | Interface to Motor – (Negative) | 2 |
| White | Output #1 to Front Headlight | |
| Yellow | Output #2 to Rear Headlight | |
| Brown or Violet |
Speaker Connections | 3 |
| Green | Output #3 / Auxiliary 1 | |
| Brown or Violet |
Output #4 / Auxiliary 2 | |
| Output #5 / Auxiliary 3 | 4 | |
| Output #6 / Auxiliary 4 | ||
| Output #7 / Auxiliary 5 | ||
| Output #8 / Auxiliary 6 | ||
| Blue | Function Common (Anode Connection, Positive) for headlights and outputs | |
| Black w/ White Stripe |
Decoder negative rail (Common ground), sink. | |
| Notes | ||
| 1 | Connection to RH, center, third Rail or overhead traction wires | |
| 2 | Connection to LH rail | |
| 3 | Either colour could have been used prior to this definition. Either colour can be used but it must be documented. | |
| 4 | Any colour other than those defined may be used, but must be identifiable and documented. | |
Reference:
21MTC Interface
- Main article: 21MTC
The 21MTC Connector interface is a standard adopted by both the NMRA and NEM 660. Its name comes from 21 pin Marklin/Trix Connector, developed by Marklin and ESU. It is often found in locomotives with OEM decoders from ESU. There are differences between the NMRA and NEM definitions for this interface.
In December 2020 the NMRA updated their interface standards and has adopted the NEM definitions as the official NMRA standard for the 21MTC connector. In time all 21MTC multifunction decoder manufactures will incorporate the combined NEM/NMRA 21MTC interface. Older models and multifunction decoders may still be available which follow the older (now superseded) NMRA pin assignments. Verify the pinouts before installing a decoder.
This interface is always a direct-connect type as there is no wiring harness. The decoder plugs directly on to the male header mounted on the locomotive chassis.
The NMRA standard has discouraged the use of this connector in new locomotive designs from January 2010. It is intended to be replaced by the PluX interface.
The main physical difference between the 21MTC and PluX decoders is the pin arrangement. The 21MTC features a female socket which mates with pins on the locomotive interface. The PluX is the opposite: the pins are on the decoder, which mate with a female connector on the locomotive. The PluX standard defines the length of the pins, as they pass through the locomotive interface board for a lower profile installation. Verify the alignment with the documentation that came with the decoder, as the connection may not be keyed to prevent incorrect alignment.
If a manufacturer states the locomotive comes with a 21-pin decoder, it would indicate a 21MTC interface.
Next18 Interface
- NEM 662 / RCN-118
- NMRA S–9.1.1.5
MOROP created the Next18 standard for extremely tight applications, such as TT and N scale locomotives. The NMRA has not embraced the Next18 interface, though some manufacturers have. In addition to specifying the electrical interface and connectors, the NEM 662 standard also mandates the maximum physical size of decoders. A fully compliant Next18 decoder is no larger than 15mm x 9.5mm - one would fit on a dime; a Next18S decoder is no larger than 25mm x 10.5mm.
| Connection | Length | Width | Height |
|---|---|---|---|
| Next18 | 15 mm | 9.5 mm | 2.9 mm |
| Next18-S | 25mm | 10.5 mm | 4.1 mm |
There are two variants: Next18 and Next18–S. Next18 supports motor control, front and rear headlights and 6 auxiliary output functions; two of those function pins may be used to provide an on-board TrainBus serial interface. A Next18–S decoder sacrifices two auxiliary function outputs for the speaker connections.
The interface specifies an extremely small 18-pin "encapsulated" connector. The entire connector is only 8mm long and 5mm wide. Because of their small size, connector pins are only rated for 500 milliamps, so some connections are allocated two pins. The result being that although there are 18 pins, some are redundant, and the 18 pins provide only 12 discrete connections. A feature of the interface is "smokeless symmetry". Pins are assigned in a somewhat symmetric fashion, such that if installed backward, no harm is done to either the locomotive or the decoder; it will not function properly, but nothing will be "smoked".
- This interface supports SUSI using pins 5, 6, 14 and 15.
- A multifunction decoder can be used as a function only decoder, as the decoder has internal circuitry to allow this.
Doehler and Haass offers a range Next18 (and 21MTC) adaptors. See their website.
Pinouts of the Next18 and Next18-S
The pinouts are symmetrical, so the decoder can be plugged in either way. AUX 3 to 6 are logic level signals. If functions work incorrectly, the decoder is installed backwards.
| Next18 / Next18–S Pin Assignments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | ||||
| Name | Next18 | Pin | Next18–S | Group |
| Track, Right | Connection to right hand rail | 1 | Connection to right hand rail | 1 |
| Motor + | Motor connection 1, Positive/Forward | 2 | Motor connection 1, Positive/Forward | 2 |
| AUX1 | Output 1 | 3 | Output 1 | 3 |
| AUX3 | Output 2 | 4 | Output 2 | 4 |
| GND | Decoder Ground connection after rectification | 5 | Decoder Ground connection after rectification | |
| V+ | Decoder positive supply, after rectification | 6 | Decoder positive supply, after rectification | |
| AUX 6 / Output 6 | 7 | Speaker B | 4 or 5 [2] | |
| F0f | Headlight forward | 8 | Headlight forward | 3 |
| Track Left | Connection to left hand rail | 9 | Connection to left hand rail | 1 |
| Track Left | Connection to left hand rail | 10 | Connection to left hand rail | 1 |
| Motor – | Motor connection 2, Negative/Reverse | 11 | Motor connection 2, Negative/Reverse | 2 |
| AUX2 | Output 2 | 12 | Output 2 | 3 |
| AUX4 / TBDATA | Output 4 | 13 | Output 4 | 4 |
| GND | Decoder Ground connection after rectification | 14 | Decoder Ground connection after rectification | |
| V+ | Decoder positive supply, after rectification | 15 | Decoder positive supply, after rectification | |
| AUX 5 / Output 5 | 16 | Speaker A | 4 or 5 [2] | |
| F0r | Headlight Reverse | 17 | Headlight Reverse | 3 |
| Track, Left | Connection to right hand rail | 18 | Connection to right hand rail | 1 |
| S-9.1.1.5 Next18 & Next18–S Multifunction Decoder Interface | ||||
| Description of Signals, NEXT18 / NEXT18-S | |
|---|---|
| Group 1 | Track, Right (pins 1 & 18) and Left (9 & 10) connect to vehicle wheels for its incoming power supply. |
| Group 2 | When a multifunction decoder is not present, Pin 2 (Motor +) normally connects to the right rail and Pin 11 (Motor –) to the left rail |
| Group 3 | Open Collector/Drain outputs which are switched to ground on the decoder's side. Voltage is supplied from pins 6 and 15 (V+) In situations where the taillights are not connected to the headlight circuit, taillights for the forward direction (Cab1) connect to AUX1, reverse direction (Cab2) connect to AUX2. Maximum current draw is 100mA per output. |
| Group 4 | Members of this group are TTL Logic Levels |
| Group 5 | Effective load presented by the speakers to the multifunction decoder must be 4 – 8Ω, and must be documented. Impedance of speakers provided with the decoder must be documented (NEXT18–S) |
SUSI Interface
For SUSI, only four signals may be used
- GND
- V+
- Train Bus Clock
- Train Bus Data
Track connections are not to be used for this purpose. All other connections can provide functions to a SUSI module.
- See NMRA T1-9.2.3 for details.
Operations Without a Next18 Multifunction Decoder Installed
For minimal operations, a dummy plug can be used.
The plug must connect pins 1, 2 and 18 together, and the same for 9, 10 and 11.
Bridge Plugs: These can be constructed to power for head and taillights.
See the associated NMRA Technical Notes and Standards for more information.
Usage as a Function Only Decoder
NEXT18 multifunction decoders may be used in an unpowered (unmotored) vehicle for the purposes of controlling functions; in this instance the decoder must have the necessary means of generating the required Service Mode Acknowledgement defined in S-9.2.3.
Web Links
- S-9.1.1.5 Next18 Next18-s Decoder Interface.pdf
- TN-9.1.1.5 Next18 Next18-s Decoder Interface.pdf
- TI-9.1.1 DCC Interface Specifications
These links are in German:
- Normblatt RCN-118 des Verband der Hersteller Digitaler Modellbahnprodukte (VHDM)
- Normblatt 662 der MOROP
Next18 Adaptors
- Doehler & Haass Next18 Adaptors
- ESU Adapter board Next18 for 6 amplified outputs. With soldering pads and wires
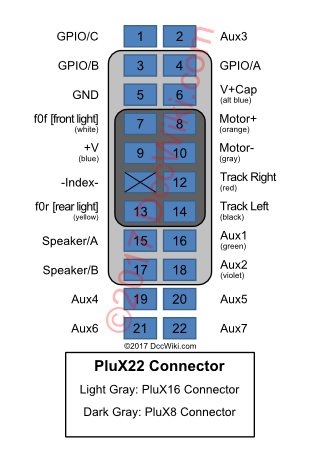
PluX Interfaces
- Main article: PluX Interface
The NMRA and MOROP have adopted a newer standard interface called PluX22, and its subsets, PluX16 and PluX8. (MOROP's NEM 658 also defines PluX12, however, NMRA Standard S-9.1.1 does not.)
Purpose
The purpose is to provide a uniform interface for safe, secure and rapid installation of decoders adhering to the PluX Standard.
Description
The PluX22 connector consists of two rows of 11 pins. PluX16 and PluX8 connectors consist of two rows of 8 pins and 4 pins respectively. The smaller connectors are subsets of the larger interface. Mechanically, the interface defines male pins on the decoder which are meant to interface directly with a female connector on a locomotive's receiving board. The preferred board-to-board orientation being that the decoder pins pass through holes in the receiving board's PCB and enter the bottom of the female connector. This would keep the height to a minimum.
- PluX8 offers no advantages over the NEM 651 interface, so it not used.
- The interface is designed for direct plug-in installation. Connection via a cable is not provided for, and are outside the PluX Standard.
- The Standard sets maximum dimensions for the decoder -- both footprint and thickness. This allows for small, drop-in decoders.
- The PluX interface supports one motor, up to 9 function outputs and one sensor input.
- Also defined are the installation space and size of the decoder. Packaging must be labelled indicating a PluX16 or PluX22 device.
E24
This is new interface from ESU. Not much detail is known about it at this time. It uses a J3200 connector that was used on the iPhone 6's camera. This is not a proprietary connector, it just hasn't been through the standardization process yet.
It is mainly used in their multifunction decoders designed for N Scale applications. If allows a lower profile and more connections than the Next18 interface. The ESU 53900 decoder tester includes this interface.
It is found on the LokSound 5 Nano, and the forthcoming LokPilot Nano.
| E24 Pinout | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| DCCWiki.com | |||
| Molex 5050702422 | |||
| Function | PIN | PIN | Function |
| Track Left | X1B | X1A | Track Left |
| P AUX11/SUSI Data | 24 | 1 | Speaker – |
| P AUX12/SUSI Clock | 23 | 2 | Speaker + |
| GND | 22 | 3 | GND |
| P AUX3 | 21 | 4 | Motor - |
| P AUX4 | 20 | 5 | |
| P AUX10/Sensor | 19 | 6 | Motor + |
| VCC | 18 | 7 | |
| U+ | 17 | 8 | V+ Cap |
| AUX 5 (Power) | 16 | 9 | LampF (Power) |
| AUX 6 (Power) | 15 | 10 | LampR (Power) |
| AUX 7 (Power) | 14 | 11 | Aux 1 (Power) |
| AUX 8 (Power) | 13 | 12 | Aux 2 (Power) |
| Track Right | X2B | X2A | Track Right |
Note: AUX3, AUX4, AUX10 - 12 are logic level (0-5V) outputs. All others are powered. Source: ESU Data Sheet. No warranties expressed or implied as to the accuracy of the table.
More Information (MOLEX): SlimStack Board-to-Board Receptacle, 0.35mm Pitch, SSB RP Series, 0.60mm Mated Height, 2.00mm Mated Width, 24 Circuits, Armor Nail
Choosing the best Decoder Format for your Model
Additional Reading
- See the NMRA Standard S-9.1.1 for more information on connectors used to create various locomotive interfaces.
- Sources for Connectors for DCC Decoders
- MOROP NEM 651 Standard (in German) defining the European 6-pin DCC interface.
- MOROP NEM 652 Standard (in German) defining the European 8-pin DCC interface.
- MOROP NEM 654 Standard (in German) defining the European 4-pin DCC interface.
- MOROP NEM 658 Standard (in German) defining Plux22, Plux16, PluX12, and PluX8. (Google translation to English)
- MOROP NEM 660 Standard (in German) defining the 21MTC Interface. (Google translation to English)
- MOROP NEM 662 Standard (in German) defining the Next18 Interface. (Google translation to English)
Adapters
For more adapters, see the Other DCC Equipment List.
Decoder Buddy
A 21MTC adapter board is available from NixTrains called the Decoder Buddy.
This interface board works with decoders by Digitrax, ESU, SoundTraxx, and TCS, as well as other 21MTC decoders.
The Decoder Buddy replaces the standard DCC 8-pin loco motherboard.
Features:
- 10-pin socket and plug with wire-outs for all 21-pin decoder functions
- 10-pin plug fully removable for easy separation of loco shell and chassis
ESU
ESU offers a number of interface adapters which allow modern multifunction decoders to be used in older locomotives:
- 21MTC Interface Part # 51967 has a socket for plugging in a multifunction decoder, with solder points for connecting to the original wiring of the locomotive.
- 51968 or 51957, adapter board with transistor amplified outputs AUX3 to AUX10.
- 51958, adapter board for PluX22
- 51999, Adapter board Next18 for 6 amplified outputs. With soldering pads and wires
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 This connection on the socket (in the locomotive) may be left unconnected, or may be connected to an an accessory. If connected to an accessory, the accessory must be protected by a diode, if it is polarity sensitive, to avoid any damage in case the plug is inserted the wrong way into the socket. On the plug, this connection may be left unconnected or may be connected to connection 7 or may be connected to a decoder’s function output. In all cases, the use of this connection must be documented by the manufacturer.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Next–18: Group 4, Logic level, NEXT18–S: Group 5